Mycoplasma insons
(May et al., 2007)
Etymology
Gr. n. mukes – fungus, Gr. neut. n. plasma – anything formed, N.L. neut. n. Mycoplasma – fungus form; L. neut. adj. insons – innocent (referring to the apparent commensalism of the organism)
Taxonomy
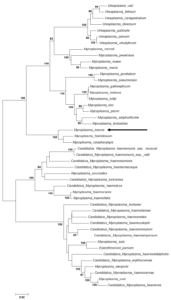
Mycoplasmatales – Mycoplasmataceae – Mycoplasma – Mycoplasma insons (not part of a cluster), effectively but not validly published, related to Mycoplasma fastidiosum (16S rRNA gene sequence similarity – 95.42%) (Fig. 1)
Type strain
I17P1T (green iguana – Iguana iguana, El Salvador, ≤2007), (Fig. 2, 16S rRNA gene sequence)
Genomes
no genome published (per 11/05/2024)
Cell morphology
twisted rods, pleomorphic
Colony morphology
umbonate
Metabolism
fermentation of glucose; non-arginine-hydrolyzing, non-urea-hydrolyzing; temperature optimum for growth is 30°C
Host
green iguana (Iguana iguana)
Habitat
upper respiratory tract
Disease(s)
unknown, considered to be a commensal so far
Pathogenicity
factors unknown
Epidemiology
unknown, once isolated from seven green iguanas from El Salvador
Diagnosis
cultivation (at 30°C) and species identification by MALDI-ToF MS or genetically
Fig. 1. Maximum likelihood tree showing the phylogenetic position of Mycoplasma insons I17P1T between the Pneumoniae/Ureaplasma and Hemoplasma cluster of Mycoplasmataceae based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. Numbers at nodes represent bootstrap confidence values (1000 replications). Only values > 80% are shown. Bar, number of substitutions per nucleotide position. Credits: Joachim Spergser (Vetmeduni Vienna)